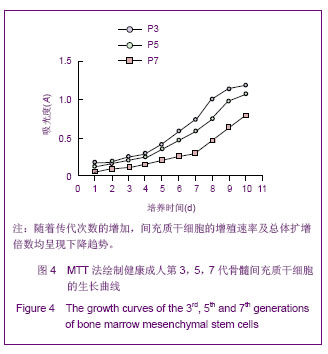
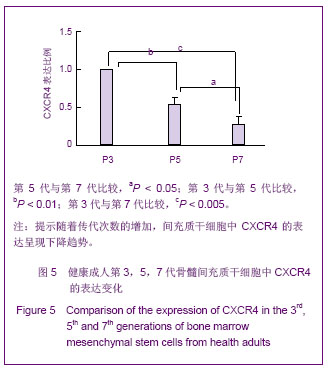
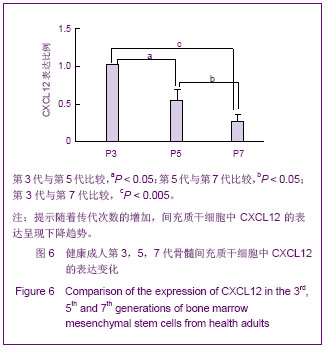
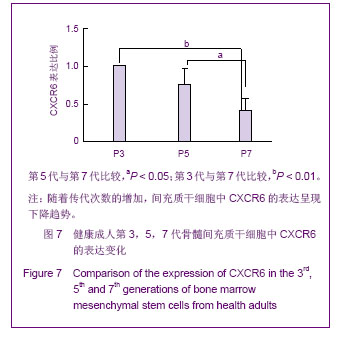
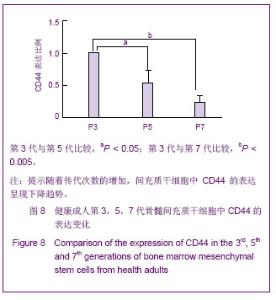
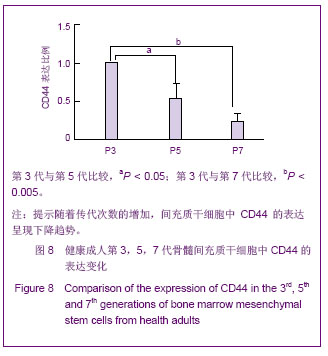
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (40): 7102-7109.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.40.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
In vitro proliferation and passage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells impact homing-associated factors
Xu Wen, Tian Chen, Li Fang, Xia Bing, Guo Qing, Zhang Yi-zhuo
- Department of Hematology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Tianjin 300060, China
-
Online:2013-10-01Published:2013-10-31 -
Contact:Zhang Yi-zhuo, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Hematology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Tianjin 300060, China aprilzyz@yahoo.com -
About author:Xu Wen★, Master, Physician, Department of Hematology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Tianjin 300060, China xuwenxuwen@hotmail.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81270603*; the Training Plan for Creative Middle-aged and Young Talents in Tianjin City*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Wen, Tian Chen, Li Fang, Xia Bing, Guo Qing, Zhang Yi-zhuo. In vitro proliferation and passage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells impact homing-associated factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(40): 7102-7109.
share this article
| [1]Qu C, Mahmood A, Lu D, et al. Treatment of traumatic brain injury in mice with marrow stromal cells. Brain Res. 2008;4: 234-239. [2]Carvalho JL, Braqa VB, Melo MB, et al. Priming mesenchymal stem cells boosts stem cell therapy to treat myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. [3]Peng L, Xie DY, Lin BL, et al. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in liver failure patients caused by hepatitis B: short-term and long-term outcomes. Hepatology. 2011;54(3): 820-828. [4]Abdel Aziz MT, Atta HM, Mahfouz S, et al. Therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on experimental liver fibrosis. Clin Biochem. 2007; 40(12): 893-899. [5]Rombouts WJ, Ploemacher RE. Primary murine MSC show highly efficient homing to the bone marrow but lose homing ability following culture. Leukemia. 2003;17(1):160-170. [6]Roland J, Murphy BJ, Ahr B, et al. Role of the intracellular domains of CXCR4 in SDF-1 mediated signaling. Blood. 2003; 101(2):399-406. [7]Lee RH, Hsu SC, Munoz J, et al. A subset of human rapidly self-renewing marrow stromal cells preferentially engraft in mice. Blood. 2006; 107(5): 2153-2161. [8]Sordi V, Malosio ML, Marchesi F, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells express a restricted set of functionally active chemokine receptors capable of promoting migration to pancreatic islets. Blood. 2005;106 (2): 419-427. [9]Sackstein R, Merzaban JS, Cain DW, et al. Ex vivo glycan engineering of CD44 programs human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell trafficking to bone. Nat Med. 2008;14(2):181-187. [10]Morrimoto K, Robin E, Le Bousse-Kerdiles MC, et al. CD44 mediates hyaluronan binding by human myeloid KG1A and KG1 cells. Blood. 1994;83(3):657-662. [11]许雯,张翼鷟 赵丹丹,等.微孔膜法比较Stro-1+和Stro-1-间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2012, 16(1):111-115. [12]Phinney DG, Kopen G, Isaacson RL, et al. Plastic adherent stromal cells from the bone marrow of commonly used strains of inbred mice: variations in yield, growth, and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 1999;72(4):570-585. [13]Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147. [14]Majumdar MK, Thiede MA, Mosca JD, et al. Phenotypic and functional comparison of cultures of marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and stromal cells.J Cell Physiol. 1998;176(1):57-66. [15]代飞,吴军,许建中,等.两种从骨髓中分离人间充质干细胞方法的比较研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2005,27(16):1631-1633. [16]颉玉欣,王旭,张进贵.间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].河北医药, 2005,27(2):130-132. [17]王蓓,汪维伟.间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].国外医学:外科学分册,2005,32(6):459-462. [18]Bianco P, Riminucci M, Gronthos S, et al. Bone marrow stromal stem cells: nature, biology, and potential applications. Stem Cells. 2001;19(3):180-192. [19]夏文杰,许茹,叶欣,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外扩增的生物学评估[J].中国实验学血液学杂志,2008,16(3):639-644. [20]Conget PA, Minguell JJ. Phenotypical and functional properties of human bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells. J Cell Physiol. 1999;181(1):67-73. [21]赛音其木格,侯相麟 赵丽,等.成人骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞的研究[J].临床血液学杂志,2005,18(4):200-203. [22]易敬林,杨海军,丁伟荣,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及其生物学特性的研究[J].江西医学院学报,2005,45(6):1-5. [23]房佰俊,韩钦,杨少光,等.TGFβ-1对成人骨髓CD105+间充质干细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].西安交通大学学报,2005,26(3):228- 231. [24]罗依,梁彬,余勤.成人骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养扩增及其生物学特性研究[J].浙江医学.2003,25(8):468-469,473 [25]Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST ,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton’ s jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1330-1337. [26]Feldmann RE Jr, Bieback K, Maurer MH, et al.Stem cel1 proteomes: a profile of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilica1 cord blood. Electrophoresis. 2005; 26(14):2749-2758. [27]Rodriguez AM, Elabd C, Amri EZ ,et al. The human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Biochimie. 2005; 87(1):125-128. [28]Wang JF, Park IW, Groopman JE. Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple focal adhesion proteins and induces migration of hematopoietic progenitor cells: roles of phosphoinositide-3 kinase and protein kinase C. Blood. 2000;95(8):2505- 2513. [29]Dalakas E, Newsome PN, Harrison DJ, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell trafficking in liver injury. FASEB J. 2005;19(10): 1225-1231. [30]Roland J, Murphy BJ, Ahr B, et al. Role of the intracellular domains of CXCR4 in SDF-1 mediated signaling. Blood. 2003;101(2):399-406. [31]Zaitseva M, Kawamura T, Loomis R, et al. Stromal-derived factor 1 expression in the human thymus.J Immunol. 2002; 168(6), 2609-2617. [32]Son BR, Marquez-Curtis LA, Kucia M, et al. Migration of bone marrow and cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in vitro is regulated by stromal-derived factor-l-CXCR4 and hepatocyte growth factor-c-met axes and involves matrix metalloprateinases. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1254-1264. [33]Shi M, Li J, Liao L, et al. Regulation of CXCR4 expression in human mesenchymal stem cells by cytokine treatment: role in homing effciency in NOD/SCID mice. Haematoiogica. 2007; 92(7):897-904. [34]Honczarenko M, Le Y, Swierkowski M, et al .Human bone marrow stromal cells express a distinct set of biologically functional chemokine receptors. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4): 1030-1041. [35]Lapidot T, Petit I. Current understanding of stem cell mobilization: the roles of chemokines, proteolytic enzymes, adhesion molecules, cytokines, and stromal cells.Exp Hematol. 2002;30(9): 973-981. [36]Petit L, Szyper-Kravitz M, Nagler A, et al. G-CSF induces stem cell mobilization by decreasing bone marrow SDF-1 and up-regulating CXCR4. Nat Immunol. 2002;3(7): 687-694. [37]Bhakta S, Hong P, Koc O. The surface adhesion molecule CXCR4 stimulates mesenchymal stem cell migration to stromal cell-derived factor-1 in vitro but does not decrease apoptosis under serum deprivation. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2006;7(1):19-24. [38]Alkhatib G, Liao F, Berger EA, et al. A new SIV co-receptor, STRL33. Nature. 1997;388(6639):238. [39]Deng HK, Unutmaz D, KewalRamani VN, et al. Expression cloning of new receptors used by simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1997;388(6639):296-300. [40]Unutmaz D, Xiang W, Sunshine MJ, et al. The primate lentiviral receptor Bonzo/STRL33 is coordinately regulated with CCR5 and its expression pattern is conserved between human and mouse. J Immunol. 2000;165(6):3284-3292. [41] Von Luttichaux I, Notohamiprodjo M, Wechselberger A, et al. Human adult CD34- progenitor cells functionally express the chemokine receptors CCR1, CCR4, CCR7, CXCR5, and CCR10 but not CXCR4. Stem Cells Dev. 2005;14(3):329-336. [42]van Beijnum JR, Rousch M, Castermans K, et al. Isolation of endothelial cells from fresh tissues. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(6): 1085-1091. [43]Young HE, Steele TA, Bray RA, et al. Human reserve pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells are present in the connective tissues of skeletal muscle and dermis derived from fetal, adult, and geriatric donors. Anat Rec. 2001;264(1): 51-62. [44]Fox JM, Chamberlain G, Ashton BA, et al. Recent advances into the understanding of mesenchymal stem cell trafficking. Br J Haematol. 2007;137(6):491-502. [45]Wu Y, Wang J, Scott PG, et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cells in wound healing: a review. Wound Repair Regen. 2007; 15(Suppl 1):S18-26. [46]Honczarenko M, Le Y, Swierkowski M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells express a distinct set of biologically functional chemokine receptors. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4): 1030-1041. [47]Shi M, Li J, Liao L, et al. Regulation of CXCR4 expression in human mesenchymal stem cells by cytokine treatment: role in homing efficiency in NOD/SCID mice. Haematologica. 2007; 92(7):897-904. [48]Li Y, Yu X, Lin S, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 enhances the migratory capacity of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;356(3):780-784. [49]Ma J, Ge J, Zhang S, et al. Time course of myocardial stromal cell-derived factor 1 expression and beneficial effects of intravenously administered bone marrow stem cells in rats with experimental myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005;100(3):217-223. |
| [1] | Peng Ya, Qin Yu, Yi Hongcheng, Gu Chunsong, Li Lili. Cytotoxicity assessment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-cuttlebone composite scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3943-3946. |
| [2] | Wang Canli, Jiao Zhili, Sun Yong, Sun Song. Comparison of the effects of two kinds of platelet-rich fibrins on the proliferation activity of human gingival fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1007-1012. |
| [3] | Liu Meilin, Fu Songtao, Wang Peisen, Hao Ran, Chang Bingmei, Hou Xiuying. Liposome prepared from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium for repair of skin wound in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 734-740. |
| [4] | Zhang Fei, Wang Wu, Li Hui-juan, Liu Ya-fei, Zhang Bao-gang, Pei Fu-qiang, Shao Qing-wei, Wu Zhong-yan. Biological characteristics of human placental mesenchymal stem cells isolated using two culture methods: a comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5292-5296. |
| [5] | Li Xing-tong1, Tang Hong-yan3, Ma Wei1, Yang Jin-wei1, 2, Wang Xian-bin1, Dai Yun-fei1, Li Jun-yan4, . A method of high purity primary neuron culture and high efficiency transfection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(32): 5186-5190. |
| [6] | Yu Xi, Hu Jun-tao, Lai Jie, Wang Rui-zhi, Ma Lan-lan, Tang Zhan-hong. Comparison of the biological characteristics of primary rat macrophages extracted by three methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(24): 3863-3868. |
| [7] | Yang Duo, Li Na. Effect of serum concentrations on differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into adipocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(17): 2669-2673. |
| [8] | Wang Shu-yue, Lin Fan-li, Qian Yi, Chen Xiao-qing, Liu Yang, Li Shu-tan, Cheng Yan, Xiong Hao, Huang Chun-lan. Coculture with mesenchymal stem cells facilitates the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells under different coculture modes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(13): 2068-2074. |
| [9] | Guo Zhi, Tong Chun, Chen Hui-ren . CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells and graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(9): 1456-1462. |
| [10] | Bi Yu-hu, Teng Jun-ru. Endometrial stromal stem cells: in vitro isolation, culture and biological features [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(5): 760-765. |
| [11] | Dong Jing-jing, Hu Zhu-lin, Li Yan, Sun Xiao-mei. Culture and identification of rhesus monkey bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(29): 4623-4628. |
| [12] | Huang Cheng-long, Li Qing, Wang Lei, Huang Kui, Luo Dao-wen, Xiao Jin-gang. A comparative study on two culture methods for adipose-derived stem cells from mice with osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(29): 4654-4659. |
| [13] | Jin Yu-lin, Wu Jie-ying, Lu Yan, Chen Jin-song, Li Fa-tao, Tang Jie, Liu Dong, Liang Qi-hua, Li Yan, Tang Xue-wei, Xie Gui-e, Wu Shao-qing. Isolation and cultivation of human placental chorionic-derived mesenchymal stem cells: optimization of the tissue explants method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(21): 3388-3393. |
| [14] | Zhang Xia, Du Zhi-xiang, Wang Na, Meng Ya-li. Effects of recombinant adenovirus vector expressing human lactoferrin on proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer stem-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(13): 2009-2014. |
| [15] | Liu Chao, Xu Zhi-guo, Wang Shao-hong, Cheng Hong-ling, Yang Xu-wei, Gong Bo, Liu Yang, Xu Chun-yan. Human amniotic epithelial cells: culture technology optimization and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(13): 2100-2107. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||